Understanding Bitcoin & Ethereum Basis: Key Metrics Historical Insights, and Risks
In the sophisticated realm of institutional investing, having a granular understanding of financial instruments like Bitcoin futures is essential. This blog provides colour on the Bitcoin and Ethereum basis, providing comprehensive insights and introducing key metrics and analytics to help you navigate this complex market.
What is the BTC and ETH Basis?
The basis refers to the difference between the spot price of Bitcoin and its futures price. By analyzing the basis, investors can gain insights into market sentiment or leverage, potential arbitrage opportunities, and the relative pricing of different futures contracts.
Key Metrics to Watch: Continuos Expiry Data
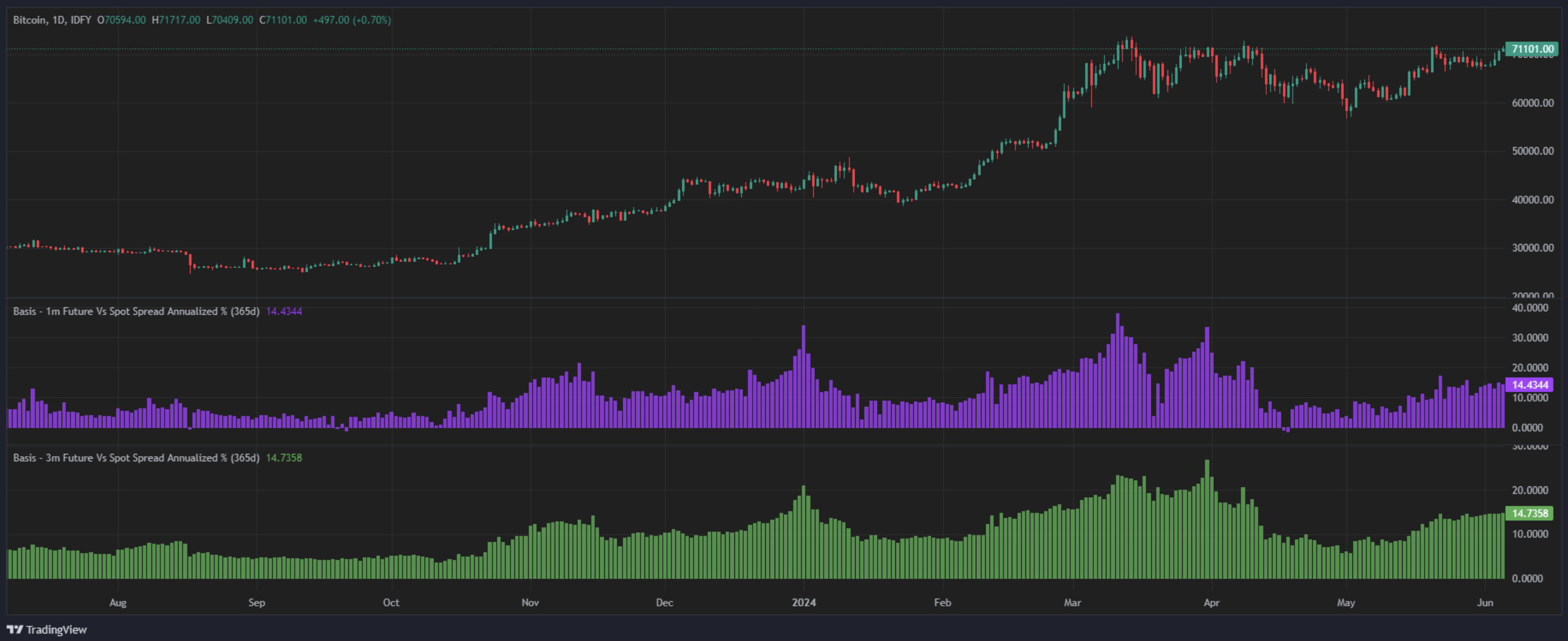
Our basis metrics focus on continuous expiry for three primary tenors: one week, one month, and three months. This allows investors to compare and contrast the basis over different time horizons, facilitating more informed trading decisions. Each tenor will deliver a different result for percent annualized return.
Our basis metrics focus on continuous expiry for three primary tenors: one week, one month, and three months. This allows investors to compare and contrast the basis over different time horizons, facilitating more informed trading decisions. Each tenor will deliver a different result for percent annualized return.
Annual Return
The annualized return metric standardizes returns over different periods, making it easier to compare the return potential profitability of various basis tenors. This metric is particularly useful for assessing the long-term potential of your investment strategies. However, don’t get fooled by large percent returns for very near-term expiries as sided pricing as well as explicit trading costs will compress that spread considerably
1 & 3 Month Futures Basis Annualised % Metrics
Spread Analysis
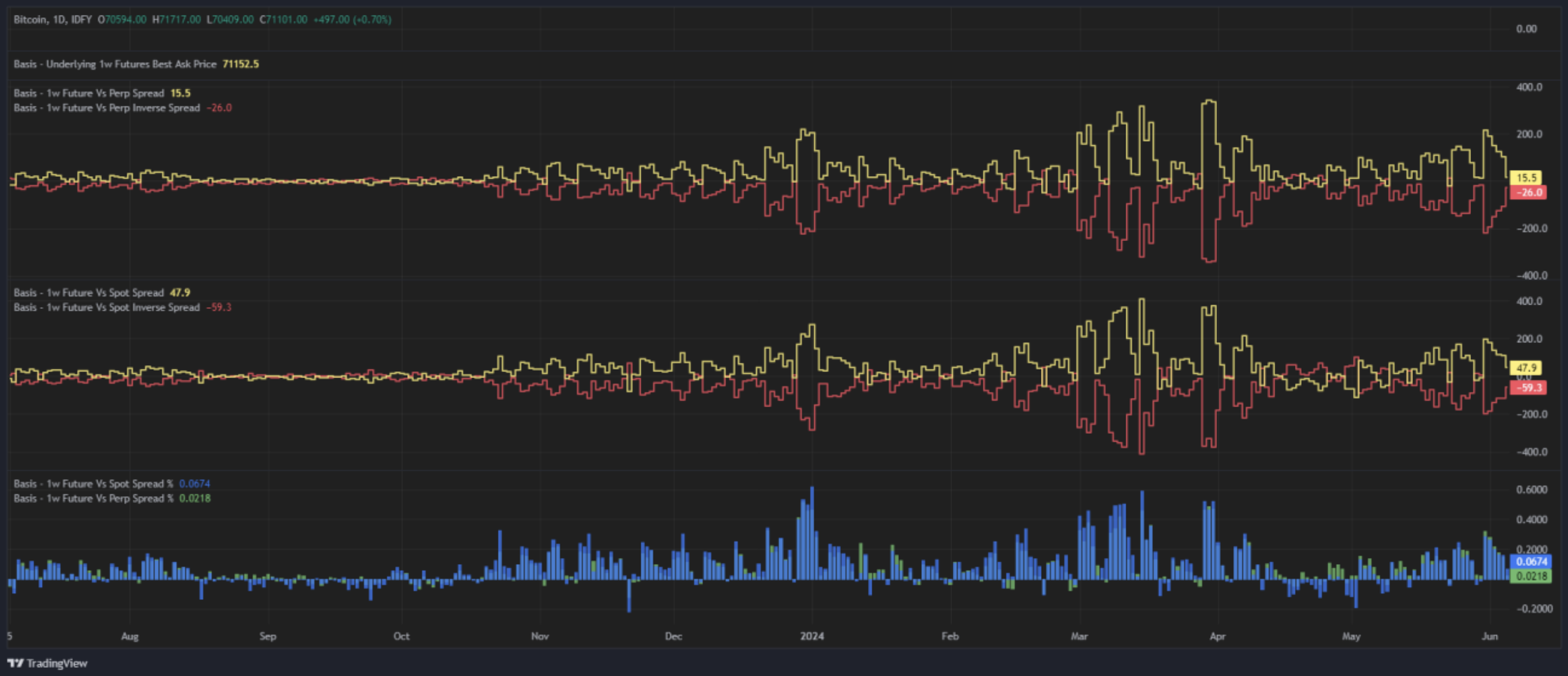
The spread, defined as the difference between the future and spot price, is a key indicator of market sentiment. A widening spread typically signals increasing leverage and demand, while a narrowing spread could indicate stabilizing conditions or the overall market growing heavy. Our detailed spread analysis helps you identify these trends and make strategic adjustments to your portfolio and analysis.
Perpetual and Spot Basis Spread and Inverse Spread metrics
Basis vs. Spot and Perpetual Futures
Comparing the basis against the spot price and perpetual futures provides further insight into funding dynamics for the perp relative to overall percent annualized return on a basis transaction. Behaviorally, basis normally favors a spot hedge in a range bound market vs strong trending as perp funding will tighten up the spread as well as apply funding costs to the long holder further reducing pnl. This comparison helps investors understand the relative value and efficiency of the different options
Spot / Perpetual Futures Basis % and $$ Spread Metrics
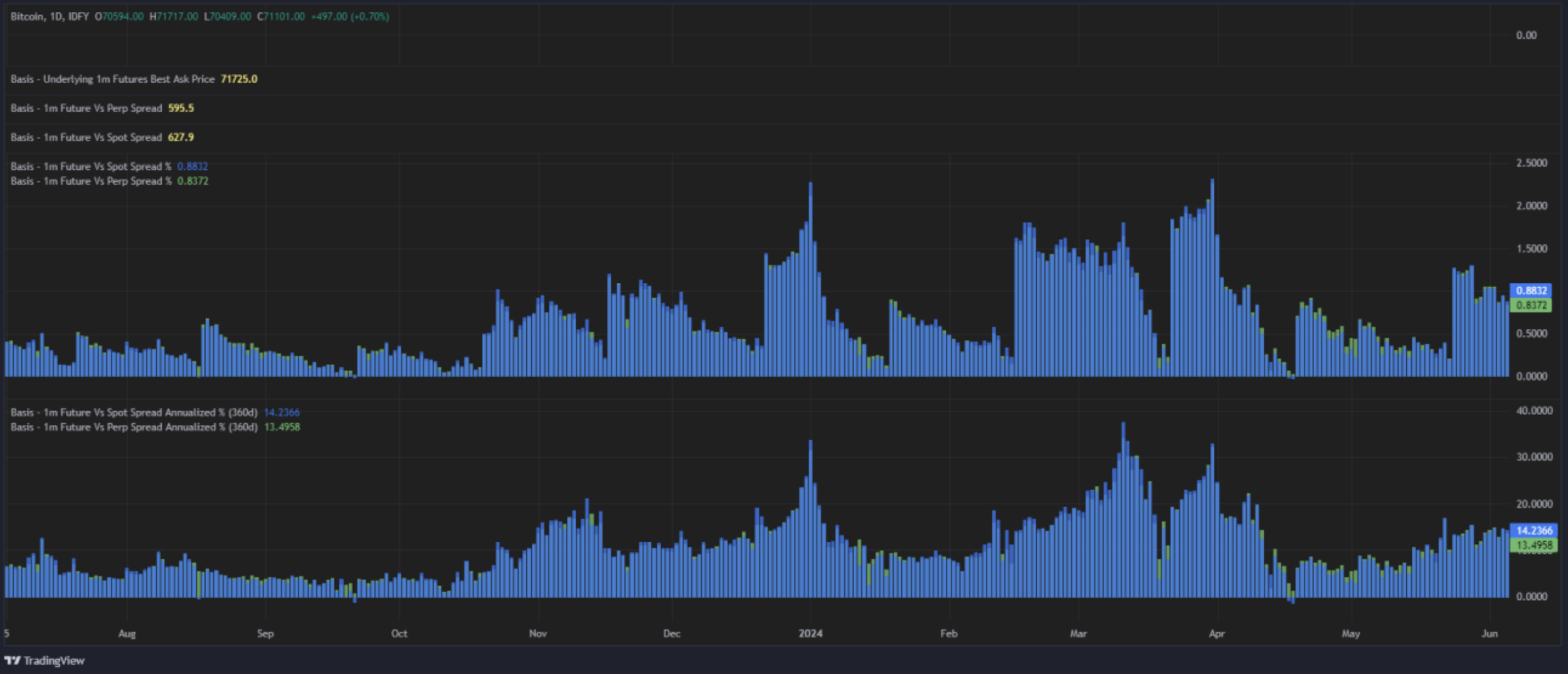
Sided Basis - What You See is Not What You Get
Top line basis can be much different than executed basis when accounting for sided pricing as well as explicit costs to transact the structure. The display below illustrates the difference between headline basis return vs sided and costed amounting in this case to roughly 1.3% for 3 month tenor.
Risks Associated with Basis Trading
Trading the Bitcoin basis comes with its own set of risks that institutional investors must consider:
Market Volatility
The cryptocurrency market is known for its high volatility. Sudden price swings can significantly impact the basis, leading to execution and potential leg risk resulting in inferior basis levels than originally sought.
Liquidity Risks
An attractive basis opportunity is only as good as the liquidity available in the market. Analysing depth is tricky given the variables at play including spot depth & futures depth. Frequently, leaning into a basis transaction becomes an exercise of price discovery across direct market access and / or counterparty – high touch pricing levels. However, using Sum 3 Levels Bid/Ask metrics as a proxy along with buy and sell ratio analytics can help frame a picture on sizing the trade relative to spread, potential liquidity constraints, and best execution (DMA, Counterparty, high / low touch).
Sum 3 Levels Bid/Ask Size - Buy / Sell Ratio Metrics
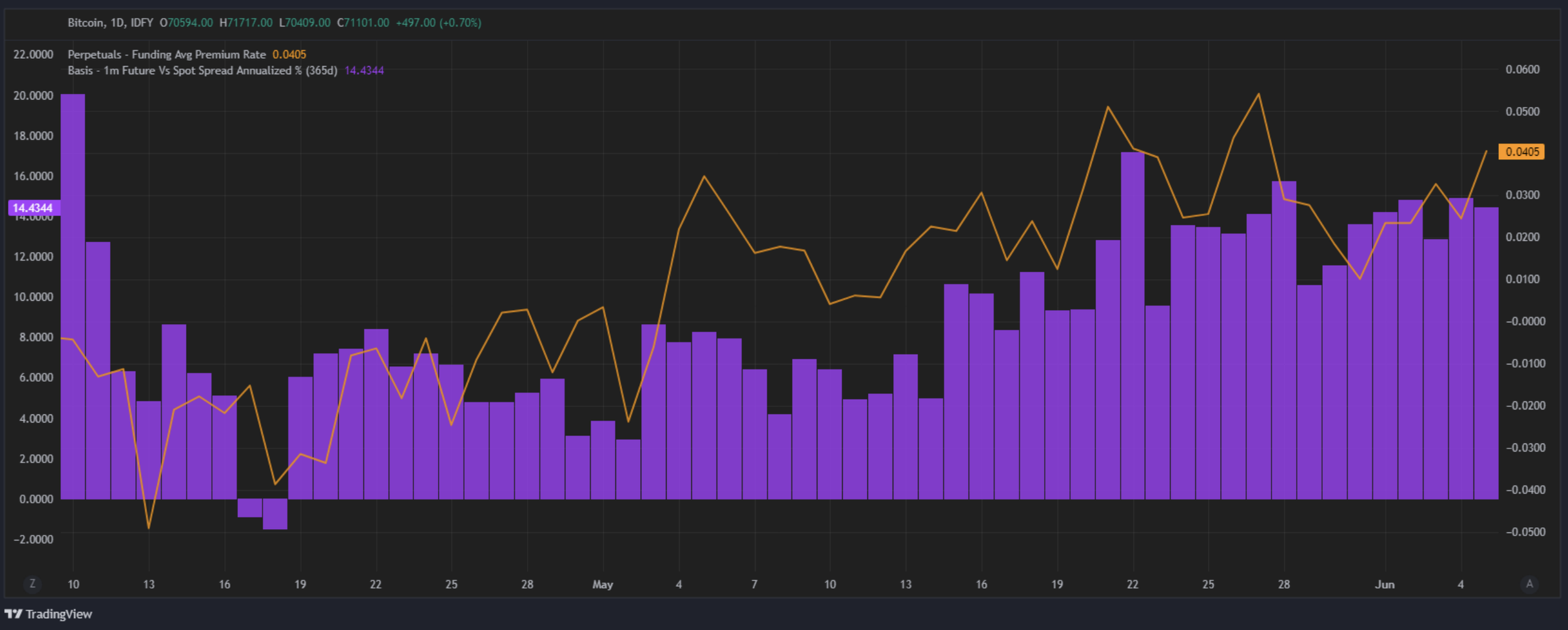
Funding Rate Risks
A basis trade can be entered into using future vs spot or future vs perpetual future. However, the latter introduces funding rate risk which may impact the performance of the trade. It is evident that when basis expands, often so too does perpetual futures funding levels as evidenced in the graph below. If you are long perp, short futures position during expansion of funding rates, your pnl on the basis will contract as funding remains elevated or increases
Perp Funding Avg Premium Rate vs Spot Futures Basis.
Execution Risks
Slippage and execution latency can impact the effectiveness of your trades, especially in a fast-moving market. Employing sophisticated trading algorithms and monitoring execution quality can help minimize these risks.
Historical Data: Learn from the Past
While real-time metrics are crucial for making immediate trading decisions, historical data provides valuable context and insights into long-term trends. By analyzing historical basis data, investors can backtest strategies, understand past market behavior, and make more informed predictions about future movements by visualizing via our user Interface or downloading historical data directly from the user interface or via rest API.
Conclusion
Understanding and trading the Bitcoin basis requires a blend of real-time data, historical insights, and a keen awareness of associated risks. By focusing on key metrics such as best bid and ask prices, annualized returns, dollar spreads, depth and risk analysis, investors can make more informed decisions and navigate the complexities of the Bitcoin and Ethereum futures market with confidence.